Migration Strategies and Models for a Seamless Transition to Cloud
According to Forbes, around 70% of cloud migration and digital transformation are not properly executed and thus end up being a disaster. So, before you decide to move to the cloud, here are a few things that you should know.
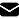
Cloud refers to the server that can be accessed over the internet and is used to run software and databases. It can help to access the same file or application from any device, as the computing takes place in the data center and not on the device or local server.
In simple terms, Cloud Migration is transferring or moving the data, applications, and other technology-related business processes from on-premise infrastructure to a cloud environment. There is a growing trend of businesses moving to the cloud, to improve operations and efficiency.
From scalability and reliability to elasticity and security, there are various benefits of migrating to the cloud. But to avail all that, you need to have a good cloud migration strategy. Before approaching a service provider, answer these three questions:
- Why do you want to migrate your business operations to the cloud?
- How will your business operations improve or benefit from migrating to the cloud?
- What are the parameters on which you will measure the success of cloud migration?
6 migration strategies that you need to consider for migration related to your requirements are:
1. Re-hosting involves migrating systems or applications as is to the cloud environment, with as few changes to the underlying system as possible. Systems that qualify for such migration during the discovery process of enterprises are deemed as quick wins due to low costs involved. However, such strategy does not make use of the features of the cloud and thus isn’t optimised to run in this new environment. This means that it may turn out to be more expensive to run this system on the cloud.
2. Re-factoring requires complete re-engineering of the system to make use of the cloud native features. Cost for this migration can be high but it can be very efficient in the long run. When categorising an application as re-factoring, the enterprise should perform a detailed business case analysis to justify cost investment and its potential impact to ensure other alternatives have been considered.
3. Re-platforming requires a few optimisations to be made, but does not alter the core architecture of an application. In such migration, one can simply migrate a database as is to another already managed platform. So, one would get the benefit of managed services such as patching database, backup and restore, automated failover, etc.
4. Repurchasing is moving to different products with the help of software as a service (SaaS).
5. Retire means to get rid of a portion of an enterprise’s IT portfolio which is not useful. This helps in redirection of attention to things users really use.
6. Retain is a strategy to revisit to migrate an application another time. This means postponing migration of an application for later consideration. It’s normal for organizations to retain some applications during their cloud migration efforts.
Choosing the right cloud model for your business is critical as well as quite challenging. It is because every business operation has unique needs, and the model should properly align with them. There are a few factors that you should consider before choosing a cloud model like, the degree of control, level of security, scalability, flexibility amongst others. Alongside documenting business processes, vigilance must be kept on security measures to prevent data loss.
Here are the 3 models that you can choose from, depending upon the individual business needs:
1. Private Cloud - If you want to have full control and access to the data, you can choose private cloud. But building a private cloud is not so easy, you need a team of experts. Plus, a high cost is involved in implementing the model. And this is why only 63% of the surveyed organizations choose to have a private cloud model.
2. Public Cloud - If your requirements are just limited to management and infrastructure issues, you can choose public clouds available in the market. In this model, the service provider handles and manages the cloud on your behalf, but there is only a reasonable level of security. It offers various services like Iaas and PaaS.
3. Hybrid Cloud - Hybrid cloud is the combination of both, i.e., you can get the features of a public cloud with security and control of a private cloud. Also known as the new private model, the number of hybrid cloud users has increased to 82%.
An enterprise should keep the following things in mind before migrating to the cloud:
- Hybrid and multi-cloud migration minimizes the risk of data loss and makes the process more efficient.
- A software change should add value to the cloud-environment. Unnecessary changes can reduce efficiency.
- Efficient data storage can help in reducing costs. Also, no hacker can take the advantage of any weakness in the cloud.
Just like each business, each migration is unique. Understand the needs and requirements of the businesses properly before you choose the migration model.
| Copyright © 2026 Manupatra. All Rights Reserved. |




























 Toll Free No : 1-800-103-3550
Toll Free No : 1-800-103-3550 +91-120-4014521
+91-120-4014521